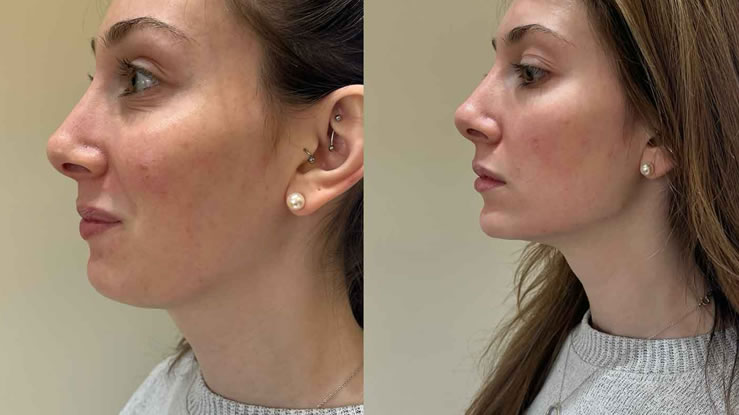
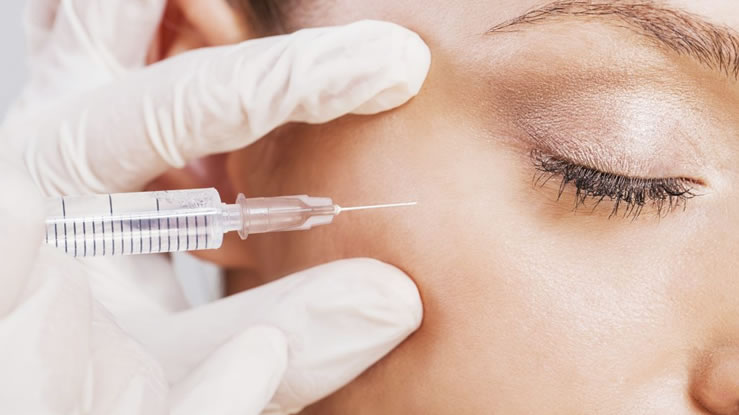
Plastic surgery and cosmetic surgery are often used interchangeably, but they are not the same. While both specialties deal with enhancing or reconstructing parts of the body, they have distinct purposes and training. Understanding the difference between plastic surgery and cosmetic surgery can help clarify which approach might be right for you based on your personal needs or goals.
Definition and Purpose
Plastic Surgery
Plastic surgery is primarily focused on reconstructing facial and body defects due to birth disorders, trauma, burns, disease, or accidents. The goal of plastic surgery is to restore the function and appearance of affected areas. It’s often medically necessary to improve quality of life, such as repairing a cleft lip or reconstructing a breast after a mastectomy.
- Key Focus: Reconstructive surgery
- Common Procedures:
- Breast reconstruction
- Burn repair surgery
- Cleft palate repair
- Hand surgery
- Scar revision surgery
Cosmetic Surgery
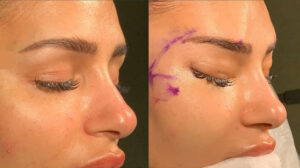
Cosmetic surgery, on the other hand, is dedicated to enhancing a person’s appearance. It is elective and aimed at improving aesthetic appeal, symmetry, and proportion. Cosmetic surgery can be performed on almost any part of the body, but unlike plastic surgery, it is not necessary for functional reasons.
- Key Focus: Aesthetic enhancement
- Common Procedures:
- Facelifts
- Breast augmentation
- Rhinoplasty (nose job)
- Liposuction
- Botox and fillers
Training and Certification
Plastic Surgeons
Plastic surgeons undergo extensive medical training, including at least 6 years of specialized surgical training after medical school. They are certified by the American Board of Plastic Surgery (ABPS) in the U.S. and similar organizations in other countries. The certification ensures that the surgeon is proficient in performing reconstructive and cosmetic procedures, although reconstructive surgery is the primary focus.
Cosmetic Surgeons
Cosmetic surgeons can come from various medical fields, such as dermatology, general surgery, or gynecology, and receive additional training in cosmetic procedures. They are certified by the American Board of Cosmetic Surgery (ABCS) or similar institutions, but this is a separate board from the ABPS. Unlike plastic surgeons, cosmetic surgeons may not always have completed the same extensive surgical training.
Procedure Focus
Plastic Surgery Procedures
Plastic surgery is focused on restoring the body’s form and function. The primary goal is often to repair or reconstruct areas that have been damaged by injury, illness, or congenital defects. Although some plastic surgery procedures may have aesthetic benefits, these are secondary to restoring the patient’s normal appearance and functionality.
- Examples:
- Skin grafts for burn victims
- Reconstructive surgery after traumatic injuries or cancer treatments
- Hand surgery to restore mobility or address congenital deformities
Cosmetic Surgery Procedures
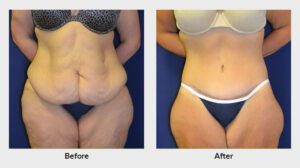
Cosmetic surgery solely focuses on enhancing physical appearance. These procedures are not medically necessary and are typically elective, meaning the patient chooses to undergo the surgery for aesthetic reasons.
- Examples:
- Tummy tucks to remove excess skin and fat
- Breast lifts to enhance breast shape
- Non-invasive treatments like Botox, laser resurfacing, and chemical peels
Goals and Expectations
Plastic Surgery:
The primary goal is functional improvement. Although there is a cosmetic benefit to plastic surgery, the intent is often to restore normal appearance or correct deformities.
Cosmetic Surgery:
The goal is purely aesthetic, with the intent of improving overall appearance, symmetry, and proportion. Patients seek cosmetic surgery to change features they are unhappy with, whether due to aging, genetics, or lifestyle.
Insurance Coverage
Plastic Surgery:
Since plastic surgery is often medically necessary, many procedures are covered by health insurance, especially in cases where reconstructive surgery is needed due to accidents, birth defects, or medical conditions like cancer.
Cosmetic Surgery:
Cosmetic surgery is generally not covered by health insurance because it is considered elective and not medically necessary. Patients usually bear the full cost of procedures such as facelifts, breast augmentations, and liposuction.
Key Takeaways:
- Plastic surgery focuses on reconstructive procedures, often necessary for medical reasons, such as trauma or birth defects.
- Cosmetic surgery focuses on aesthetic enhancements to improve appearance, symmetry, and proportion.
- Plastic surgeons typically undergo more comprehensive surgical training than cosmetic surgeons.
- Insurance coverage is more likely for plastic surgery, while cosmetic surgery is generally paid for out of pocket.
Both plastic and cosmetic surgery play essential roles in helping people achieve their desired appearance, whether for medical or aesthetic reasons. Understanding the differences allows individuals to make more informed choices when considering surgery, ensuring they choose the right type of surgeon and procedure for their needs.