Invasive procedures form the foundation of traditional surgery and medical practice. Unlike minimally invasive or non-invasive options, invasive procedures involve breaking the skin, entering body cavities, or manipulating internal tissues to achieve medical or cosmetic goals. They remain essential in healthcare whether it’s saving lives, correcting deformities, or transforming appearance through cosmetic surgery.
While technological innovations have made many procedures less invasive, some conditions and goals still require full surgical intervention for optimal results. Let’s explore what defines invasive procedures, their different types, examples in both medical and cosmetic contexts, and what to expect from them.
Understanding Invasive Procedures
An invasive procedure refers to any medical or surgical treatment that requires entry into the body. This can mean cutting through the skin, inserting instruments into body cavities, or directly operating on internal organs.
These procedures are typically performed in sterile, controlled environments such as hospitals or surgical centers under local or general anesthesia. They are carried out by highly trained medical professionals and may involve longer recovery times compared to non-surgical alternatives.
Why Invasive Procedures Are Necessary
Despite the rise of minimally invasive and non-surgical options, invasive procedures remain critical for several reasons:
-
They allow direct access to tissues, organs, and structures that require repair or removal.
-
They provide permanent or more dramatic results for certain conditions.
-
They’re essential for diagnosing or treating complex diseases.
-
In cosmetic surgery, they can offer transformations that less invasive options cannot achieve.
Categories of Invasive Procedures
Invasive procedures can be classified into two broad categories:
-
Medical Invasive Procedures: Performed to treat illness, injury, or disease.
-
Cosmetic Invasive Procedures: Performed to enhance or alter physical appearance.
Let’s take a deeper look at both.
Medical Invasive Procedures
Medical invasive procedures are often life-saving or medically necessary. These can range from routine operations to complex surgeries involving multiple organs.
1. Open-Heart Surgery
This is one of the most invasive and intricate medical procedures. Surgeons open the chest to operate on the heart often to repair valves, clear blocked arteries, or correct congenital defects. Though newer, less invasive techniques exist, open-heart surgery remains vital for severe cardiac conditions.
2. Organ Transplants
Organ transplantation involves removing a diseased or failing organ and replacing it with a healthy donor organ. Common examples include kidney, liver, heart, and lung transplants. It’s a highly invasive procedure that requires significant precision and post-surgical care.
3. Brain Surgery (Craniotomy)
A craniotomy involves opening part of the skull to access the brain. It’s performed for tumors, aneurysms, or trauma-related injuries. Due to the brain’s delicate structure, these surgeries are among the most complex in the medical field.
4. Cesarean Section (C-Section)
A cesarean section is a common invasive procedure where an incision is made through the abdomen and uterus to deliver a baby. Though routine, it involves major abdominal surgery with a recovery period of several weeks.
5. Laparotomy
A laparotomy involves making a large incision in the abdomen to explore, diagnose, or treat abdominal problems such as intestinal blockages, tumors, or organ perforations.
6. Orthopedic Surgeries (Joint Replacement, Spinal Surgery)
Joint replacement surgeries, such as hip or knee replacements, involve removing damaged bone and cartilage and replacing them with prosthetic parts. Spinal surgeries can involve fusing vertebrae or correcting deformities.
7. Hysterectomy
This is the surgical removal of the uterus and sometimes surrounding tissues, often due to fibroids, cancer, or severe endometriosis.
8. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgeries
While these are often associated with aesthetics, reconstructive procedures like cleft palate repair, skin grafts for burn victims, and tissue reconstruction after accidents or mastectomies are medically essential.
Cosmetic Invasive Procedures
Cosmetic invasive procedures have transformed the world of beauty and self-image. They focus on reshaping, enhancing, or rejuvenating the body’s appearance through surgery. Unlike non-surgical treatments that provide subtle changes, invasive cosmetic surgeries deliver more defined and long-lasting results.
1. Liposuction
Liposuction involves inserting a thin tube called a cannula under the skin to suction out fat from targeted areas like the abdomen, thighs, or arms. It remains one of the most popular cosmetic surgeries worldwide.
2. Breast Augmentation
This involves inserting implants (silicone or saline) under the breast tissue or muscle to enhance size and shape. It’s often chosen for aesthetic enhancement or post-mastectomy reconstruction.
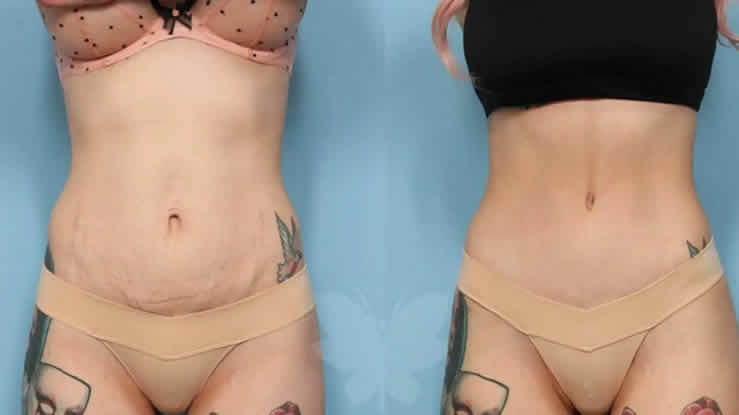
3. Tummy Tuck (Abdominoplasty)
A tummy tuck removes excess fat and skin while tightening abdominal muscles. It’s a common choice after pregnancy or major weight loss.
4. Rhinoplasty (Nose Surgery)
Rhinoplasty reshapes or reconstructs the nose for aesthetic or functional reasons (such as improving breathing). It’s a delicate procedure that significantly changes facial balance.
5. Facelift (Rhytidectomy)
A facelift tightens sagging facial skin, smooths wrinkles, and restores a youthful appearance by lifting underlying muscles and tissues.
6. Brazilian Butt Lift (BBL)
This procedure uses fat grafting, transferring fat from one part of the body (like the abdomen or thighs) to the buttocks for a fuller, more contoured appearance.
7. Blepharoplasty (Eyelid Surgery)
Blepharoplasty removes excess skin, fat, and tissue from the eyelids, rejuvenating the eye area and improving vision if drooping skin obstructs it.
8. Hair Transplant Surgery
In hair transplantation, hair follicles are removed from one part of the scalp and implanted in thinning or bald areas. Though considered minor compared to other surgeries, it’s still invasive because it involves incisions and tissue manipulation.
How Invasive Procedures Differ from Minimally Invasive Ones
The difference between invasive and minimally invasive procedures lies in the method and recovery process. Invasive procedures typically require larger incisions, anesthesia, and hospital stays. They also have longer recovery periods and higher risks of complications.
Minimally invasive procedures, on the other hand, use smaller incisions, advanced imaging, or laser technologies to achieve results with less trauma. However, invasive surgery is often the only solution for severe medical conditions or dramatic cosmetic transformations.
Preparation for Invasive Procedures
Before undergoing an invasive procedure, patients usually go through comprehensive medical evaluations, including blood tests, imaging scans, and discussions about anesthesia risks. It’s also important to disclose any underlying health issues, medications, or allergies.
Psychological preparation is just as vital. Many people feel anxious before major surgeries, so pre-surgery consultations help patients understand the process, potential results, and recovery timeline.
Recovery and Aftercare
Recovery varies depending on the type of surgery but generally involves:
-
Hospital observation for one or more days
-
Restricted movement or bed rest
-
Pain management with prescribed medication
-
Post-surgery check-ups to monitor healing
-
Gradual return to normal activities over weeks or months
Scarring is common, but modern surgical techniques and aftercare routines such as silicone scar gels, laser therapy, and microneedling help minimize visible marks.
Risks of Invasive Procedures
Every invasive surgery carries potential risks, including:
-
Infection or bleeding
-
Blood clots
-
Adverse reactions to anesthesia
-
Nerve or tissue damage
-
Scarring or asymmetry in cosmetic results
However, with an experienced and qualified surgeon, these risks can be significantly reduced. Following aftercare instructions also plays a huge role in recovery success.
Advancements in Surgical Techniques
Medical and cosmetic surgery fields have seen significant advancements. Robotic-assisted surgery, improved anesthesia techniques, and better imaging tools have made even invasive procedures safer and more precise. Cosmetic surgeons now use hybrid approaches combining surgical and minimally invasive methods to achieve more natural-looking results.
Invasive procedures remain a cornerstone of both medical and aesthetic progress. Whether it’s saving lives, correcting deformities, or enhancing beauty, they represent the skill, innovation, and precision of modern medicine.
While non-surgical options continue to grow in popularity, certain goals still require the transformative power of full surgery. The key is to make informed choices — consult certified professionals, weigh benefits against risks, and ensure that your expectations align with the possibilities of your chosen procedure.