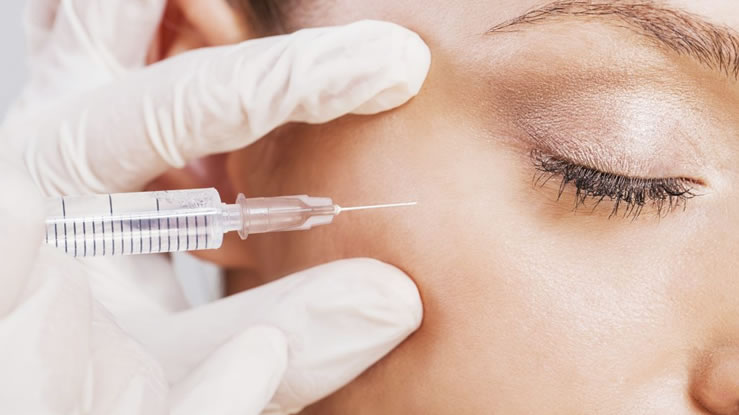
Botox has become a household name in the world of cosmetic procedures, known for its ability to reduce the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines. But what exactly is Botox, and how does it work? In this article, we’ll delve into the science behind Botox, its uses, benefits, and what you can expect from the treatment.
What is Botox?
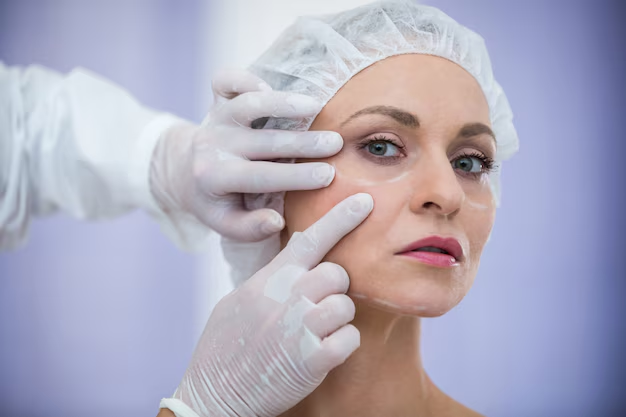
Botox, short for botulinum toxin, is a neurotoxic protein produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. Although it is known for its cosmetic applications, Botox has been used for various medical treatments since the late 1980s. It is administered in small doses to temporarily paralyze specific muscles, preventing them from contracting.
How Does Botox Work?
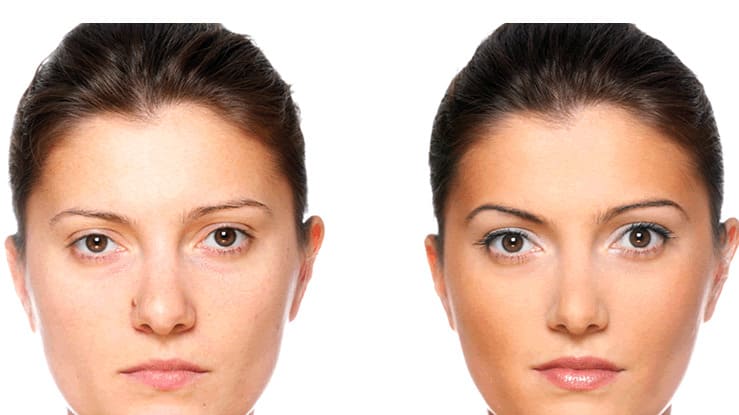
When injected into the skin, Botox blocks the signals from nerves to the muscles. This prevents the muscles from contracting, which in turn relaxes the overlying skin. The result is a smoother appearance, particularly in areas where wrinkles are formed by repetitive muscle movements, such as:
- Forehead lines
- Crow’s feet (lines around the eyes)
- Frown lines between the eyebrows (glabellar lines)
The effects of Botox typically become visible within a few days and can last anywhere from three to six months, depending on the individual and the area treated.
Common Uses of Botox
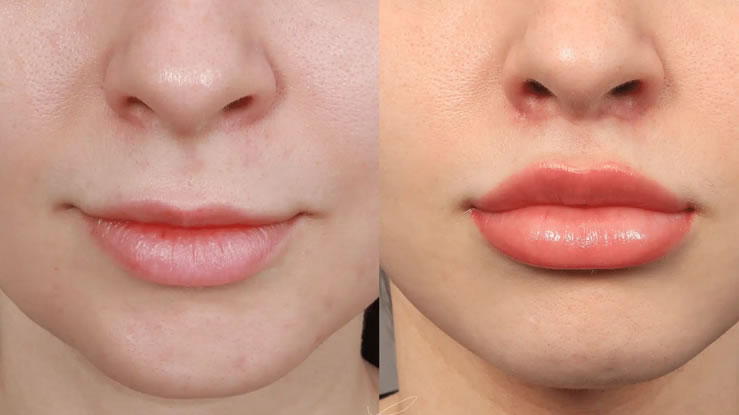
1. Cosmetic Applications
The most well-known use of Botox is for reducing facial wrinkles. It’s particularly effective for:
- Dynamic Wrinkles: These are wrinkles that form due to muscle movements, such as smiling or frowning.
- Preventative Treatments: Many people in their 20s and 30s opt for Botox as a preventive measure to delay the onset of wrinkles.
2. Medical Uses
Beyond aesthetics, Botox has several medical applications, including:
- Migraine Treatment: Botox injections can help reduce the frequency and severity of chronic migraines.
- Excessive Sweating (Hyperhidrosis): Botox can block the nerves responsible for sweat production, providing relief for those who experience excessive sweating in areas like the underarms, hands, and feet.
- Muscle Spasms: Botox is used to treat various muscle disorders, including cervical dystonia (a painful condition where the neck muscles contract uncontrollably).
- Overactive Bladder: It can help manage symptoms of overactive bladder by relaxing the bladder muscles.
Benefits of Botox
- Quick and Minimally Invasive: Botox treatments are relatively quick, often taking only 10 to 15 minutes, with minimal downtime.
- Natural-Looking Results: When administered by a qualified professional, Botox can provide subtle, natural-looking results without a drastic change in appearance.
- Long-Lasting Effects: Results can last for several months, making it a cost-effective option for many.
What to Expect During the Procedure
- Consultation: Before the treatment, you’ll have a consultation with a qualified healthcare provider to discuss your goals, medical history, and any concerns.
- Preparation: The treatment area will be cleaned, and a topical anesthetic may be applied to minimize discomfort.
- Injection: Using a fine needle, the provider will inject small amounts of Botox into the targeted muscles. You may feel a slight pinch during the process.
- Post-Treatment Care: After the injections, you can typically resume normal activities immediately, although it’s advised to avoid strenuous exercise and lying down for a few hours.
Potential Side Effects
While Botox is generally considered safe, some people may experience side effects, including:
- Bruising or swelling at the injection site
- Headaches
- Temporary drooping of nearby muscles (if injected incorrectly)
- Allergic reactions (rare)
Botox is a versatile treatment that offers both cosmetic and medical benefits. Understanding what Botox does and how it works can help you make informed decisions about whether it’s right for you. Always consult with a qualified professional to ensure safe and effective treatment tailored to your needs. With the right approach, Botox can be a powerful tool in achieving your desired aesthetic and health goals.